BIOMECHANICAL EXAM
Bio-me-cha-nics
The study of the mechanical properties of the human body that affect its movements.
A biomechanical exam, what is it?
A biomechanical exam is a comprehensive assessment of the way the human body functions while walking and while practicing sports. Both static and dynamic tests are conducted to investigate the body’s osteo-articular and muscular functions.
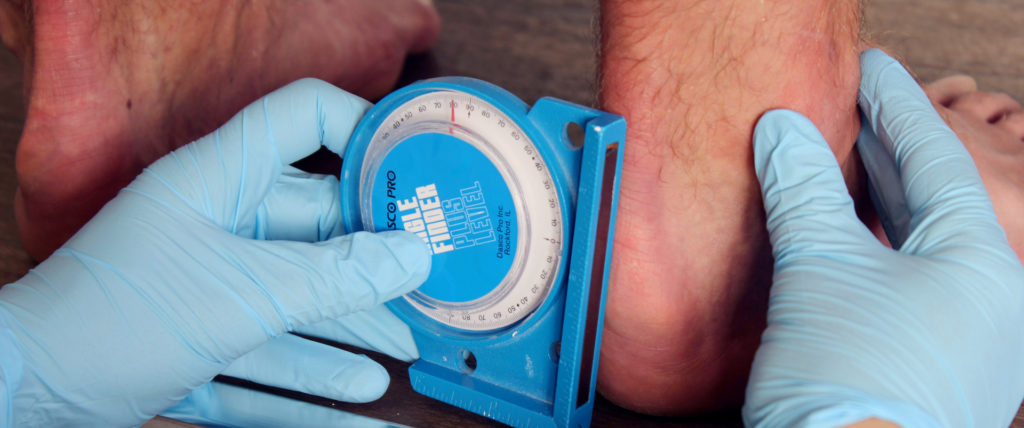
In addition to a physical and clinical assessment, a podiatrist will examine the patient’s biomechanics with the help of pressure analysis imaging technology including sensors embedded in shoes and/or placed on the floor with cameras as well as X-ray imaging.
This information is then analyzed in order to identify the source of the problem, establish a podiatric diagnosis and ultimately develop of an appropriate treatment plan.
A biomechanical exam, who is it for?
A biomechanical exam is an indispensable tool in the following cases:
- Plantar misalignment (flat foot, high arches or abnormal arches)
- Pain in the back, ankles, legs, knees, hips or feet
- Excessive accumulation of calluses and hard skin under the feet
- Abnormal or excessive wear and tear of shoes
- Athletes aiming to optimize their performance and prevent injuries
- Athletes wishing to identify the source of biomechanical pain
- Verifying normal development in children
- Persons of all ages who wish to ensure optimal foot health and posture
What are the earnings of a biomechanical exam?
- Efficiently identifies the mechanical abnormalities of the patient
- Supports a more accurate diagnosis and the identification of underlying causes
- Helps the patient better understand the issue since the results of the analysis are explained on the spot
- Supports the development of an appropriate and personalized treatment plan
- Provides a holistic assessment of the foot and lower limb function
- Provides an overall picture of the patient’s posture
-
Patient history and physical exam:
Review of the patient’s medical history and functional tests performed standing or lying down.
-
Computerized gait and posture analysis:
A number of determining biomechanical factors are assessed using pressure sensors connected to cameras.
-
Digital X-rays and related exams:
Various angles are measured to better evaluate bone alignment. Additional exams are sometimes necessary to establish a more exact diagnosis (e.g. diagnostic ultrasound, scanogram,etc).
-
The condition and personalized treatment plan are explained:
Your podiatrist provides you with an overview of your foot health and suggests a treatment plan based on your needs.
A foot scanner is enough to investigate my feet and make appropriate orthotics!

These generic foot “scanners” produce an image of plantar pressures while you are standing. However, this two-dimensional photography does nothing to explain the source of these pressures! To make an appropriate treatment such as orthotics, a comprehensive study of the feet in static and dynamic is needed, in standing position, walking and lying down.
For example, a foot with a very high arch can produce the same print as one with a fallen arch.
My orthotist (or orthesist) has the same training as a podiatrist to conduct biomechanical exams.

Even though orthotists have an adequate college-level training in the general biomechanics of the human body, podiatrists have doctorate degree and deeper knowledge of the feet and their function. In contrary to orthesists, podiatrists can prescribe further testing, like X-rays and other imaging tests. Finally, they also have the skills to establish a podiatric, medical diagnosis in addition to prescribing a treatment plan.