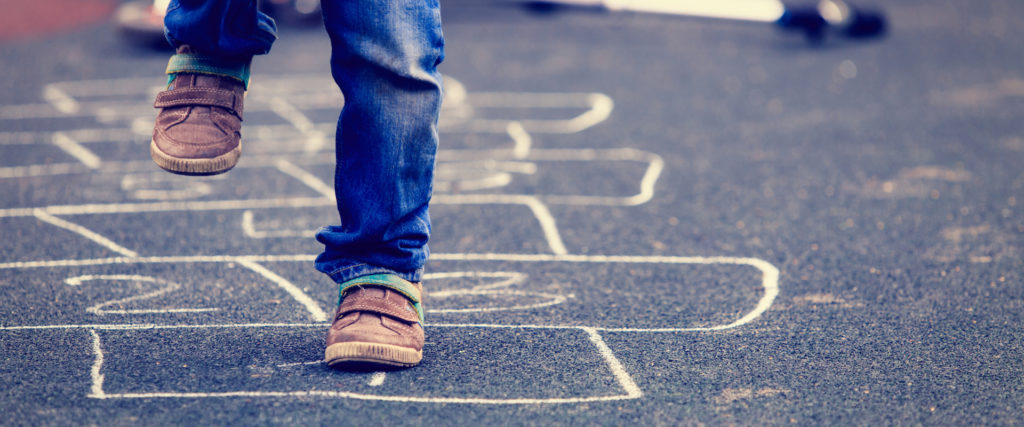
Children with flat feet
Children are born with lots of fatty tissue in their plantar arches, giving the appearance of flat feet. Normally, the arches of the feet form gradually, becoming more apparent around the age of three. From there, the feet continue developing until they attain their adult appearance. However, some children’s feet don’t develop adequately and remain flat, leading to postural deficiencies with the potential to cause problems in the future.
See the causes See the long term complications See how to relieve yourself at home
Signs and symptoms of flat feet in children
Because children complain of pain less frequently than adults, it’s important to be attentive to other signs and symptoms:
- Fallen arches
- Poor ankle alignment
- Shoes wear down and lose form quickly
- Fatigue when walking or during physical activities; the child asks to be carried
- Unstable feet and ankles; sprains may occur
- Abnormal gait
- Feet point inward
- Walking on tiptoes
- Frequent falls
- Poor balance
- Difficulty keeping up with other children their age during physical activities
- “Growing pains”: leg pain at night; the child asks for massages
- Pain in the knees, hips or back
- Occasionally, pain under the arches of the feet, at the heel or at the ankles
What are the causes of flat feet in children
A number of factors may contribute to flat feet. Whether the condition is hereditary, due to bone structure or a consequence of leg alignment, a whole host of factors should be considered:
- Ligamentous laxity
- Hypermobility of the bones in the feet
- Family history of flat feet
- Poor bone development in the feet
- Bowed legs
- Internal hip rotation
- Short Achilles tendon
- Blocked ankles
- Inadequate supporting muscles and/or hypotonia
- Tarsal coalition
- Compensation for a leg length discrepancy
- Tibial or femoral torsion (internal or external)
- And many others
Progression and consequences of flat feet in children
Because the feet are the foundation for posture, any misalignment spreads like a domino effect: the ankles turn inward, which in turn leads to the excessive internal rotation of the shins and knees. And since the knees are connected to the hips by the femur bone, the entire pelvis experiences internal rotation, causing the back to curve and generating instability across the entire lower limb region. Thus, flat feet can impact muscular-skeletal and postural development in a growing child.
It’s also at a young age that our brain is “programmed” to unconsciously perform certain movements, like walking, running and jumping. In children with flat feet, the wrong muscles get engaged. As a result, a faulty muscular activation sequence is learned. The more years pass, the more difficult it becomes to change these established patterns.
When the foot is collapsed, the bones of the foot lose their congruence and fail to offer a stable foundation, making movement inefficient and difficult. As a comparison, we’ve all experienced how much harder it is to walk on an unstable surface, like sand, than on a sidewalk. That’s because a sidewalk provides a solid foundation, so walking is easier and requires less energy. Children with flat feet are thus at a disadvantage when it comes to physical activity, as they have to expend more energy to compensate for their poor mechanical function. They tire more quickly and are less likely to participate in sports activities.
Finally, flat feet lead to a multitude of problems in adulthood.
The following is a non-exhaustive list of some of the most common problems:
- Bunions (hallux valgus) and hammertoes
- More frequent sports injuries
- Plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome
- Achilles tendinitis
- Tibialis posterior tendinitis
- Chronic pain caused by poor posture (in the ankles, knees, hips and back)
- Sprains and ankle instability
- Morton’s neuroma
- Capsulitis and metatarsalgia
- Osteoarthritis and calcification
How to relieve a flat feet pain at home
As your toddler’s feet develop, it’s advisable to let them stay barefoot as often as possible. Also, choose flexible shoes that leave a lot of space for the toes. This ensures adequate stimulation of the plantar muscles and balance function, particularly when the infant plays on irregular surfaces like grass or sand.
However, if the child’s feet are flatter than average, if walking or running is especially difficult or if frequent falls occur, it’s advisable to get firmer shoes with more support, as these provide greater stability and can diminish excessive collapsing of the feet. But even in cases of flat feet, the child should be allowed to go barefoot from time to time, especially when playing on irregular surfaces, to help develop their balance.
In addition, if your child presents one of the signs and symptoms of flat feet, certain exercises can help stimulate and improve their balance.
If your child suffers from flat feet, it’s a good idea to get them involved in sports, even if they’re hesitant to participate. Sports can help them strengthen their muscles, improve their balance and learn better muscular activation sequences.
Diagnostic of flat feet in children
- A complete biomechanical exam is essential in assessing flat feet in children. As mentioned, collapsed arches can have several causes. Therefore, it’s important to evaluate each segment in the lower limbs, verify all aspects of foot mobility, analyze posture and gait and evaluate plantar pressure. The biomechanical exam also involves taking images of posture and gait for follow-up purposes. Find out more (biomechanical exam for children).
- X-rays are also required in order to assess the alignment, length and congruence of the bones in the foot. Angle measurements are made to determine whether the child’s development is normal for their age. These measurements can be reviewed during follow-up to check if the feet are developing properly over time. In adolescence, X-rays help determine if the bones in the feet have stopped growing.
What can my podiatrist do about flat feet in children?
1. Evaluation and follow-up :
Your podiatrist has the expertise to ensure that patients’ feet develop properly. The criteria for normal development in children differ from those used for adults, and they change from year to year. Children must go through different stages of development depending on their age. Depending on the situation, your podiatrist may recommend intervention to help your child achieve proper development through exercises, splints or other treatments. Ensuring the normal development of your child’s feet is a good enough reason to pay a visit to the podiatrist. The earlier a problem is detected, the greater the potential for correcting it.
2. Footwear modifications :
If your child’s feet collapse excessively before the age of three, changes to footwear may be necessary. Infants’ feet are not developed enough to treat the condition with orthotics.
3. Plantar orthotics :
Orthotics are a preferred treatment option for children with gait problems. They are not “crutches”; they help align the feet for optimal function and stimulate a more normal course of development. In addition, pediatric plantar orthotics help children develop appropriate muscular activation sequences. Children adapt to orthotics easily and their benefit is experienced rapidly.
How to prevent flat feet in children?
To reduce the impact of flat feet on your child’s growth, it’s important to remain vigilant and intervene upon the first appearance of signs and symptoms, like abnormal gait, walking on tiptoes, inward-pointed feet, faster-than-average onset of fatigue, difficulty running as fast as other children, complaints of pain or frequent falls (see Signs and Symptoms). The longer you wait to intervene, the less can be done to influence the development of the condition.
My child has flat feet but he's still growing. Plantar orthotics can wait until he finishes growing.

False! If there's the slightest doubt, it's better to consult with a podiatrist. The more the child grows, the more their bones, muscles, ligaments and joints develop and the harder it becomes to guide their optimal growth. Orthotics may be worn from the age of three years.
And if it was not flat feet in children?
A number of foot-related problems can produce similar symptoms and issues to those of flat feet:
- Flexible high arches (“false flat feet”)
- Tibial torsion compensated by hyperpronation
- Femoral torsion compensated by hyperpronation
- Morton’s toe
- Compensatory metatarsus adductus
- Flexible anterior high arches (pseudoequinus)